The Ukraine invasion, the ensuing energy crisis and the more visible signs of climate crisis has caused the issue of climate change to truly arrive in peoples hearts and minds. The energy crisis in particular aligns three societal objectives in one policy dimension – energy savings. Households, by saving energy, can help save money, resulting in lower energy bills, contribute to saving the environment through lower CO2 emissions and at the same time, provide a material national security benefits by blunting Putin’s energy weapon. That is to say: saving the economy, saving the environment, and blunting Putin’s energy weapon is a potential pro-growth equitable alternative. The work in this research agenda is intrinsically linked to much of my other research foci over the years.

Research Output
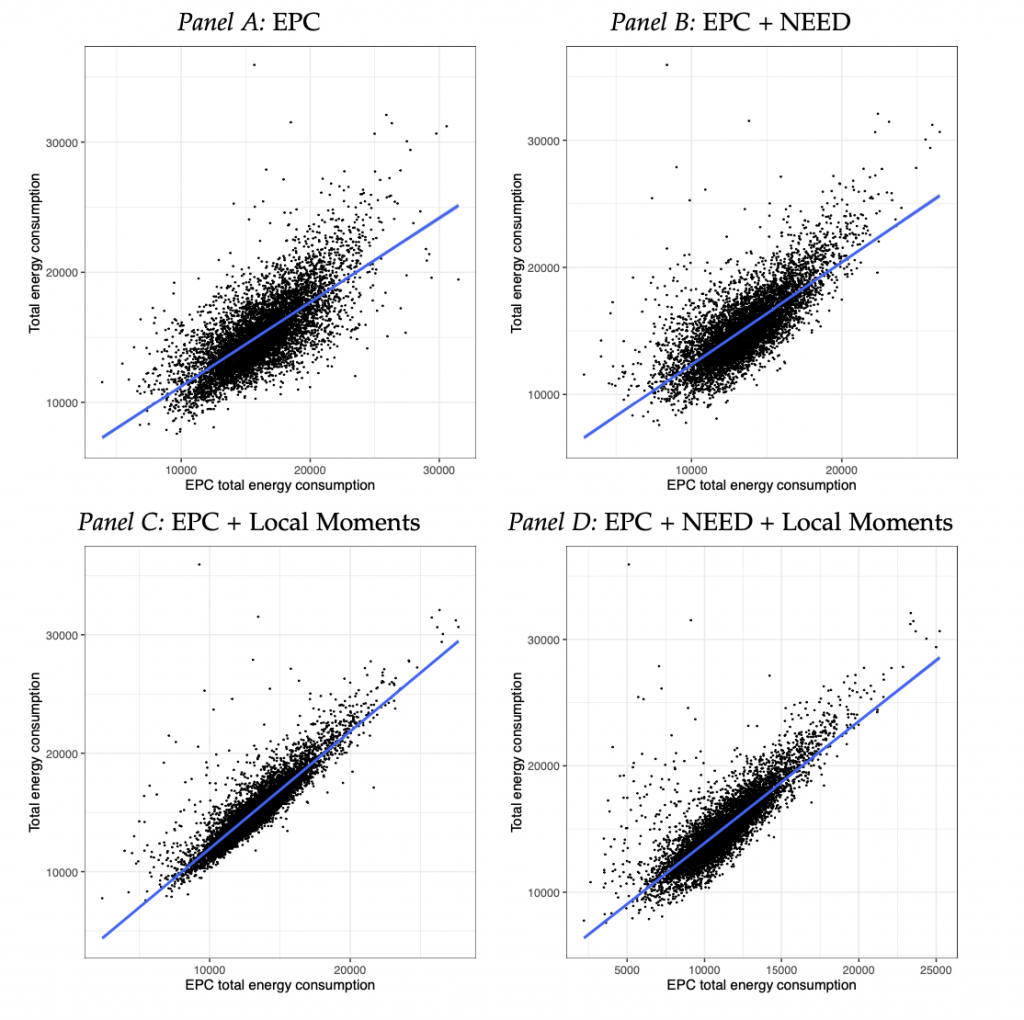
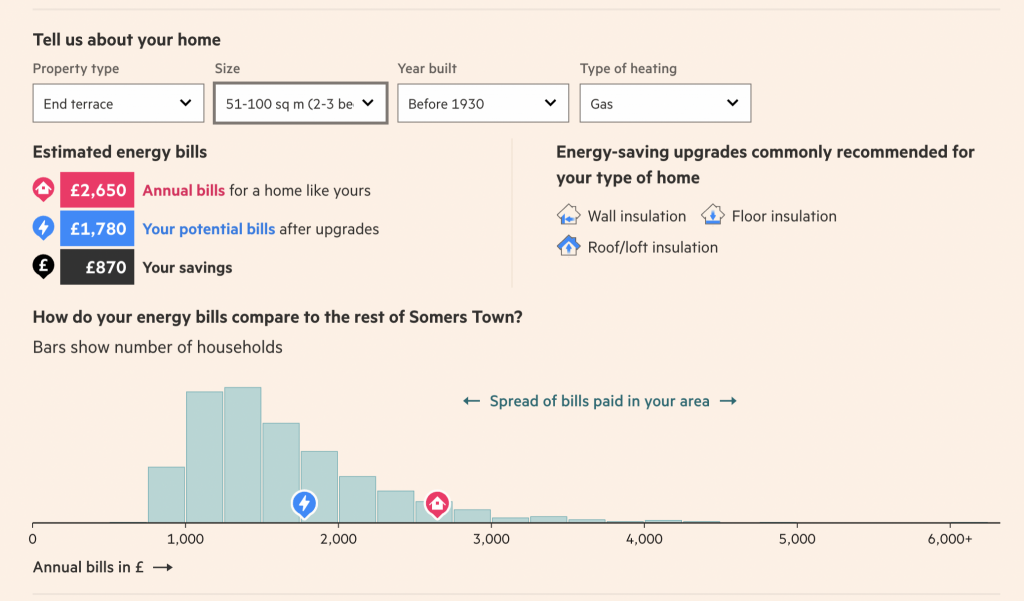
How large is the energy savings potential in the UK?, joint with Ludovica Gazze and Menna Bishop, CAGE Working Paper, 🔓 Open access.
⌨️ Blog Post
Broader coverage: Financial Times, Daily Express (1), Daily Express (2), Redmayne Bentley, Building.co.uk.
Opinion Piece: Byline Times
Context: This paper essentially develops a measurement and evaluation framework through which the impact of the energy crisis and its political handling can be empirically evaluated. This will shed some light on whether policy choices were lead by the evidence and raise questions on the relative trade-offs and the implicit welfare weights that policy makers use when designing welfare policy. This project produced the data that was used in the Financial Times visual story-telling piece linked below. An open science repository explains this work, the underlying data and the analysis steps that are intended to follow over the coming months and years.

Beyond the Energy Price Guarantee. With or without?, CAGE and NIESR Policy Briefing, 2022 , 🔓 Open access.
⌨️ Blog Post
Context: This paper walks through the UK’s policy response to the energy price shock in the wake of the invasion of Ukraine. The UK’s policy response stood out as much of it was very regressive and untargeted and in many ways may not adhere with what one would consider traditionally to be “first-best”. The policy briefing quantified the likely trade-offs, and on the event discussed a range of policy options that the UK government could have implemented that likely would have been less fiscally costly and also less distortionary.
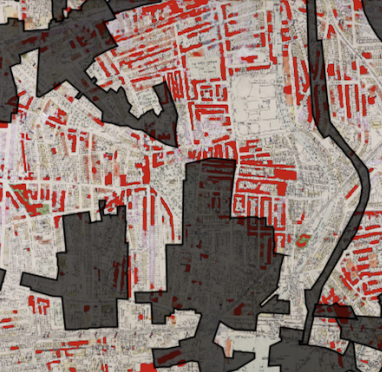
Regulatory barriers to climate action: evidence from conservation areas in England, CAGE & CEPR Working Paper, 🔓 Open access.
⌨️ Blog Post
Broader coverage: Financial Times
Context: This paper showcases how spatial institutions that can trace their origins to opposition of what would become a main driver of climate change — now poses a significant barrier on (individual) climate action.
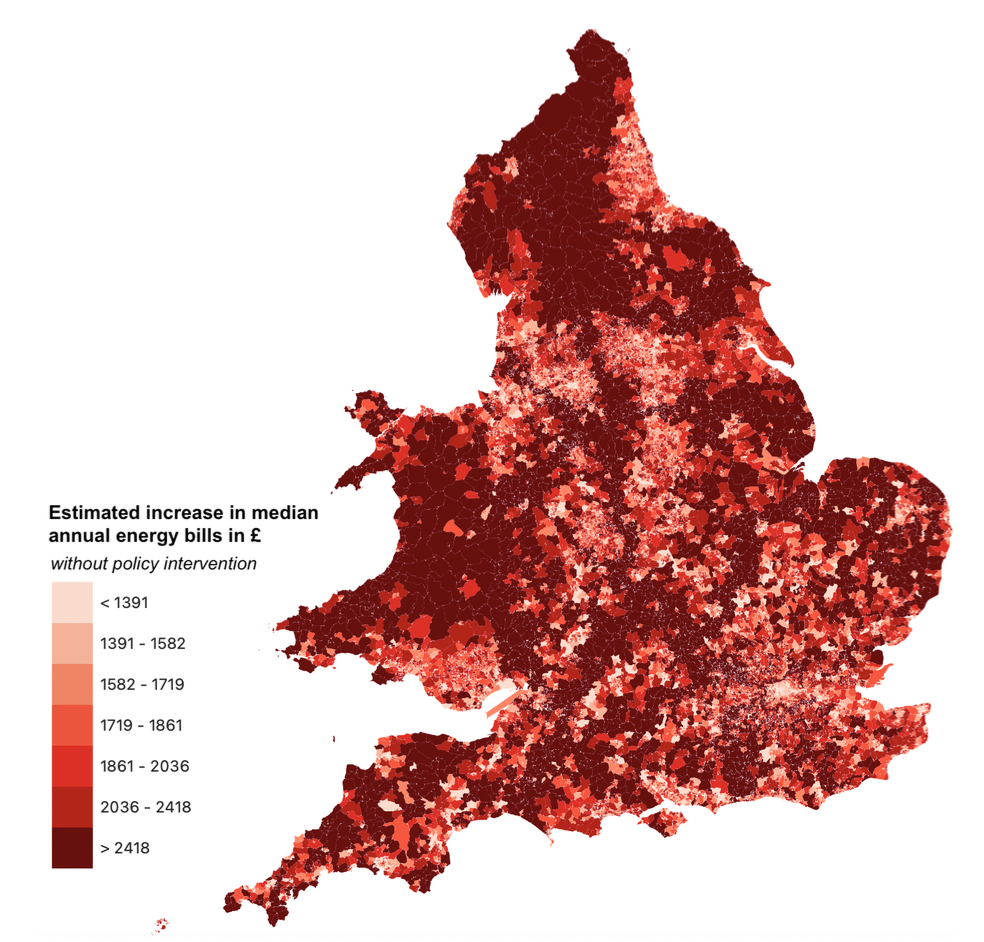
Distributional and climate implications of policy responses to energy price shocks. CAGE Working Paper & CEPR Working Paper, 🔓 Open access.
Context: This paper provides a correlational analysis of the higher dimensional correlation space casting a light on which demographic groups would likely be more exposed to by the energy crisis and how the policy interventions that were brought about by the government is limiting various socio-economic groups exposure to the energy price shock. It documents first and foremost that the energy price shock is progressive in nature, but that the intervention to lower unit prices is rendering the response much less progressive.
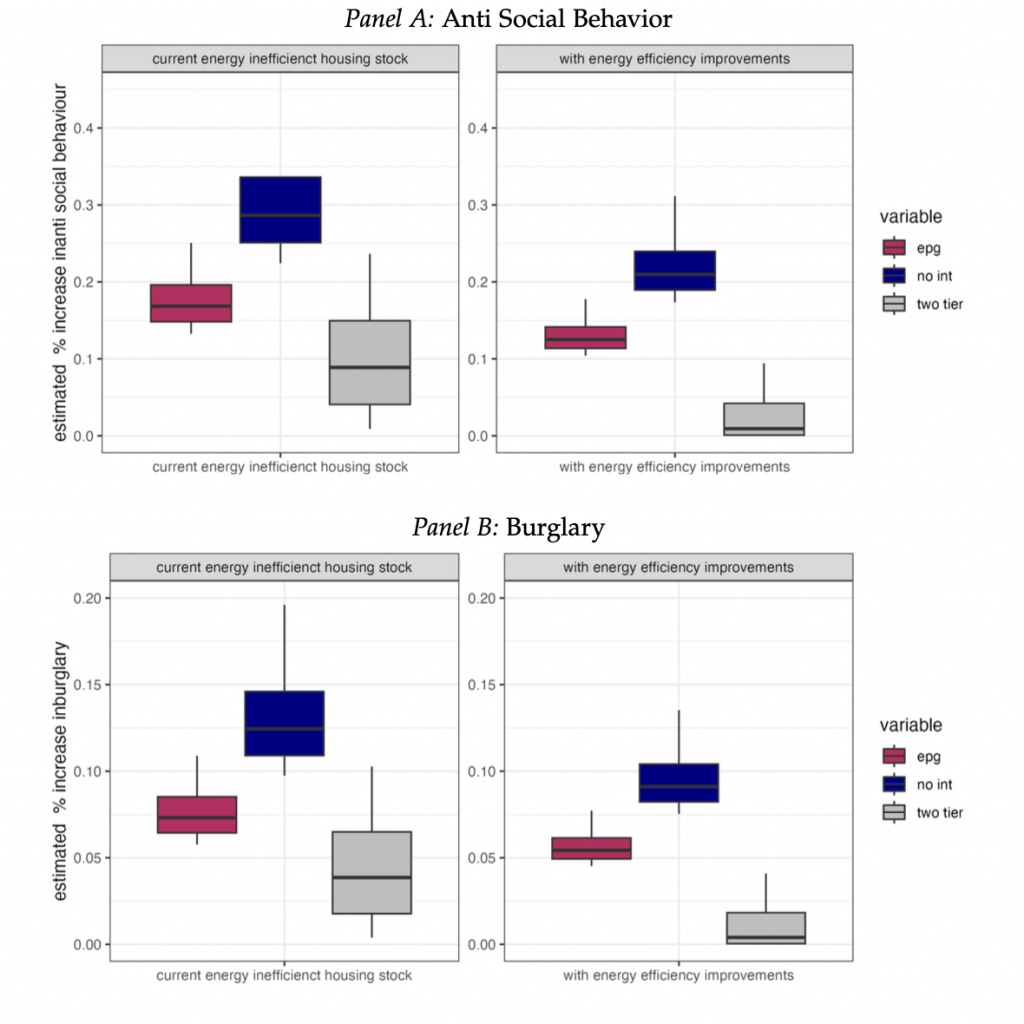
Did the policy response to the energy crisis cause crime? Evidence from England, CAGE Working Paper, 🔓 Open access.
⌨️ Blog Post
Context: This paper is the first in a whole series of short papers that will document the adverse effect that the energy crisis had on socio-economic outcomes across England. This particular paper documents how the energy price shock caused an increase in economically motivated crimes.

Informational Boundaries of the State, joint with Jacob Edenhofer and Callum Shaw. 🔓 Open access.
Context: Formal conceptions of state capacity have mostly focused on indirect measures of state capacity – by, for instance, using the state’s fiscal or extractive capacity as a proxy for its overall capacity. Yet, this input or extractive view of state capacity falls short, especially since cross-country empirical evidence suggests that similar levels of fiscal capacity, measured by tax revenues as a percentage of GDP, can produce starkly different outputs – both in classic economic terms and in broader terms that citizens would recognize as desirable outcomes, including quality of life, health, security, equality of opportunity, and intergenerational mobility. This paper argues that a central step towards addressing these shortcomings of the conventional view is to account for a crucial and largely ignored boundary of the state or dimension of state capacity: its capacity to gather, process, and deploy information in its conduct of fiscal policy. Specifically, we study how the presence or lack of such informational capacity constrains governments in responding to crises, such as the recent energy price shock. Our framework provides the analytical toolkit to examine how the informational boundary of the state shapes the incentives for policymakers to resort to untargeted and/or distortionary policy instruments, as opposed to targeted and non-distortionary ones, in responding to crises. The policy response to the energy crisis following the invasion of Ukraine provides the empirical context upon which we bring this theoretical framework to bear on data, though the latter can be straightforwardly extended to other recent crises.

Network Determinants of Cross-Border Media Coverage of Natural Disasters, joint with Prashant Garg. 🔓 Open access.
Interactive website: Transnational Natural Disaster Reporting
Context: Climate change is increasing the frequency and severity of natural disasters worldwide. Media coverage of these events may be vital to generate empathy and mobilize global populations to address the common threat posed by climate change. Using a dataset of 466 news sources from 123 countries, covering 135 million news articles since 2016, we apply an event study framework to measure cross-border media activity following natural disasters. Our results shows that while media attention rises after disasters, it is heavily skewed towards certain events, notably earthquakes, accidents, and wildfires. In contrast, climatologically salient events such as floods, droughts, or extreme temperatures receive less coverage. This cross-border disaster reporting is strongly related to the number of deaths associated with the event, especially when the affected populations share strong social ties or genetic similarities with those in the reporting country. Achieving more balanced media coverage across different types of natural disasters may be essential to counteract skewed perceptions. Further, fostering closer social connections between countries may enhance empathy and mobilize the resources necessary to confront the global threat of climate change.
Impact
The research agenda that I set up and shared with a range of collaborators in summer 2022 will gradually unfold. The building blocks of this work have been put in motion with some randomized controlled trials, a policy briefing, an interactive dashboard, tremendous amounts of data collection. My broader title for this research agenda is the “Political Economy of Climate (In)Action”. It is explicitly left open as I would like to genuinely believe that a global consensus on action is emerging and growing. The war in Ukraine, the energy crisis and the outright visibility of the climate crisis may spur people into action to bring in motion the economic transformation that is needed.
I also firmly believe that much of what needs to be done is rethinking and robustifying our institutions. While the work in this research branch is mostly using UK data, I try to draw data in from other countries to expand the breadth and scope. The UK, in many contexts is actually championing some of the necessary changes to bring about climate action moving beyond conventional mercantilistic policies. But it is also subject to its very own political economy.